
by Valerie Sicignano, NYC Feral Cat Initiative
During high kitten season in the spring and summer, it’s not unusual to discover a nest of unattended kittens or a single kitten seemingly abandoned by the mother. You want to help, right? Before jumping to the rescue, consider these recommendations.
First: Wait & Watch
You might have come across the kittens while their mother is off searching for food, or is in the process of moving them to a different location. Try to determine if the mother is coming back for them, or if they are truly orphaned.
To do this, stand far away from the kittens — 35 feet or more. If you stand too close, the mom will not approach her kittens. You might need to go away completely before the mother cat will return to attend to the kittens. It might be several hours before the mother cat returns — until she no longer senses the presence of humans hovering near her litter.
If you need to leave before the mother cat comes back, carefully evaluate whether the kittens are in immediate danger: Is it raining or snowing? Are dogs or wild animals that might harm the kittens running loose in the neighborhood? Does the neighborhood have kids or adults who are likely to harm the kittens? Are the kittens located in an area with heavy foot or car traffic?
To help with your decision, it is important to know that it might take several hours for the mother cat to return, and healthy kittens can survive this period without food as long as they are warm. Neonatal kittens are much more at risk of hypothermia than they are of starvation. During spring and summer months, waiting a longer time to see if mom will come back is much safer than during frigid winter months.
The mother cat offers her kittens’ best chance for survival, so wait and watch as long as you can. The best food for the kittens is their mother’s milk. Remove the kittens only if they are in immediate, grave danger.

If the mother cat returns…
If mom returns and the area is relatively safe, leave the kittens alone with mom until they are weaned. You can offer a shelter and regular food to mom, but keep the food and shelter at a distance from each other. Mom will find the food but will not accept your shelter if the food is nearby, because she will not want to attract other cats to food located near her nest.
Six weeks is the optimal age to take the kittens from the mother for socialization and adoption placement, and any time after eight weeks for Trap-Neuter-Return (spay/neuter, vaccination, eartip, and return to their colony). Female cats can become pregnant with a new litter even while they are still nursing, so don’t forget to get the mother cat spayed or you will have more kittens soon! Learn how to socialize kittens and how to successfully trap a mom and her kittens.
If the mother cat does not return…
If you discover that mom has been hit by a car, or if for any reason it appears that she is not coming back, then you should remove the kittens. This is crucial to the kittens’ survival. But you must be prepared to see this project through to weaning if you decide to intervene!
If you take the kittens in, it is unlikely that you will find an organization with available staff or volunteers to take on bottle-feeding on short notice. Some organizations do have experienced bottle-feeders, but prior logistical planning is necessary. Animal shelters and veterinarians generally do not take in newborn kittens, since they do not have the staff to feed and stimulate them for elimination around-the-clock.
You can contact the NYC Feral Cat Initiative at info@NYCFeralCat.org or (212) 330-0033 x5 and we will attempt to find someone to bottle-feed the kittens, but this might take days or weeks, and we might not be successful in locating a feeder. If we do find someone to bottle-feed, you might still be responsible for taking the kittens back when they no longer require bottle-feeding. You also might be responsible for paying for veterinary visits, which might include emergency medical care, and will definitely include spay or neuter surgery, disease testing, and vaccinations. And finally, you might be responsible for adopting the kittens into permanent homes. The NYC Feral Cat Initiative can help you locate low-cost veterinary care, and might be able to help you find new homes for the kittens, but completing these tasks will be your responsibility.
Kitten Care & Bottle-Feeding
First Steps
- Prepare for bottle-feeding and proper care before you take the kittens off the street.
- If you feel you must take the kittens in, wrap the carrier or container you will transport them in in a towel for warmth, but make sure you leave air holes uncovered so the kittens won’t suffocate.
- Check to see if the kittens are warm. This is more important than feeding. Never feed a cold kitten! If the kittens are cold, you will need to warm them up slowly. You can tell a kitten is cold if the pads of his feet and/or ears feel cool or cold. Put your finger in the kitten’s mouth. If it feels cold, then the kitten’s temperature is too low. This is life-threatening and must be dealt with immediately. Warm up the kitten slowly over 20 minutes by wrapping him in a towel or baby blanket, holding him close to your body, and continually rubbing him with your warm hands.
- Determine the age of the kittens by comparing them to the photos and descriptions on the How Old Is That Kitten? Kitten Progression: At-a-Glance page on the Alley Cat Allies website, or the Boutique Kittens website (Note: we do not advocate breeding or buying kittens; these kitten development photos just happen to be particularly descriptive.).
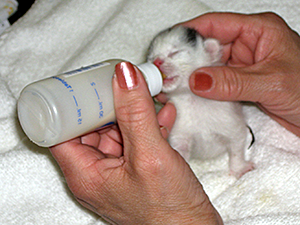
Feeding & Elimination
Neonatal kittens (under four weeks of age) cannot eat solid food (not canned, not dry) and cannot urinate or defecate on their own, so you must bottle-feed them around-the-clock and stimulate their genitals after every feeding so they can eliminate. For example, if you have kittens less than one week old, they will need to be fed and stimulated every three hours. That means you will be caring for them eight times a day — for example, at midnight, 3:00 a.m, 6:00 a.m, etc. If the kittens are unusually small or sickly, they might need to be fed every two hours.
Skipping feedings or overfeeding can cause diarrhea, which results in dehydration, a condition that can be fatal for small kittens (not to mention a hassle for you to clean up after). Diarrhea requires a visit to the veterinarian.
As the kittens age, the number of feedings they need per day goes down. You can start weaning at four weeks of age.
Milk Replacement Formulas
Powdered kitten milk replacement formula is better for kittens than the canned liquid formula. We recommend that you use only powdered kitten milk replacement formula from the start — or as soon as possible — to prevent diarrhea. Two major brands of formula are available: PetAg KMR® Powder and Farnam Pet Products Just Born® Highly Digestible Milk Replacer for Kittens. Both brands are available in both canned and powdered formulas. We highly recommend the powdered type to prevent diarrhea. It can be purchased at pet food stores, veterinarians’ offices, or online. Revival Animal Health offers the lowest prices we know of.
Make sure that the powdered formula you are using is fresh by opening the pop-top and smelling it. It should smell slightly sweet, like powdered milk. If it has a sharp smell like bad cooking oil, cheese, or chemicals, it is rancid, and dangerous to give to the kittens. Do not use any type of formula past the expiration date.
Once opened, kitten milk replacement formula (canned or powdered) must be refrigerated promptly and stored in the refrigerator. You cannot keep opened kitten milk replacement formula out of the refrigerator for very long before it spoils. Think of it as fresh milk.
Tip: Using unflavored Pedialyte electrolyte solution instead of water when mixing the powdered formula for the first 24 hours of feeding helps prevents diarrhea and eases the transition from mom’s milk to commercial kitten milk replacement formula.
Bottle-Feeding Guidance for Beginners
- Visit the the NYC Feral Cat Initiative website for detailed information on bottle-feeding orphaned newborn kittens,
- E-mail us at info@NYCFeralCat.org and describe what instructions/information you need, or
- Call us at (212) 330-0033 x5 and leave a voicemail with your name, address, and a description of what instructions/information you need.
 About the Author
About the Author
Valerie Sicignano is Community Relations Director for the New York City Feral Cat Initiative and has been working with feral cats in New York City since 1990. She holds a Certificate in Humane Education from the ASPCA, and her work with animals has been recognized by the Manhattan Pet Gazette’s “Animal Guardian Award” and In Defense of Animals’ “Companion Animal Guardian Award.”




